Doc Extractor
Definition
LLMs cannot directly read or interpret document contents. Therefore, it’s necessary to parse and read information from user-uploaded documents through a document extractor node, convert it to text, and then pass the content to the LLM to process the file contents.
Application Scenarios
- Building LLM applications that can interact with files, such as ChatPDF or ChatWord;
- Analyzing and examining the contents of user-uploaded files;
Node Functionality
The document extractor node can be understood as an information processing center. It recognizes and reads files in the input variables, extracts information, and converts it into string-type output variables for downstream nodes to call.
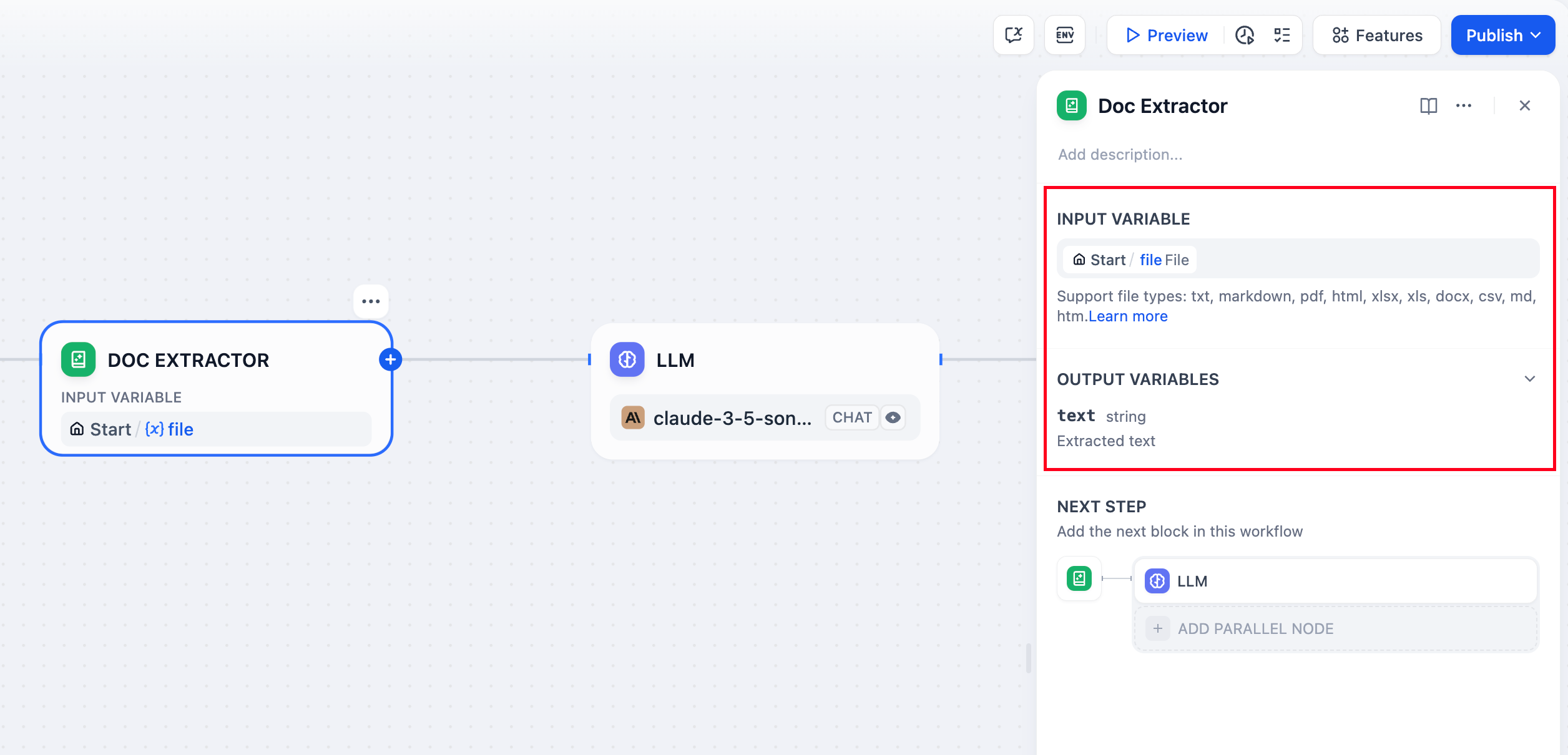
The document extractor node structure is divided into input variables and output variables.
Input Variables
The document extractor only accepts variables with the following data structures:
File, a single fileArray[File], multiple files
The document extractor can only extract information from document-type files, such as the contents of TXT, Markdown, PDF, HTML, DOCX format files. It cannot process image, audio, video, or other file formats.
Output Variables
The output variable is fixed and named as text. The type of output variable depends on the input variable:
- If the input variable is
File, the output variable isstring - If the input variable is
Array[File], the output variable isarray[string]
Array variables generally need to be used in conjunction with list operation nodes. For details, please refer to List Operator.
Configuration Example
In a typical file interaction Q&A scenario, the document extractor can serve as a preliminary step for the LLM node, extracting file information from the application and passing it to the downstream LLM node to answer user questions about the file.
This section will introduce the usage of the document extractor node through a typical ChatPDF example workflow template.
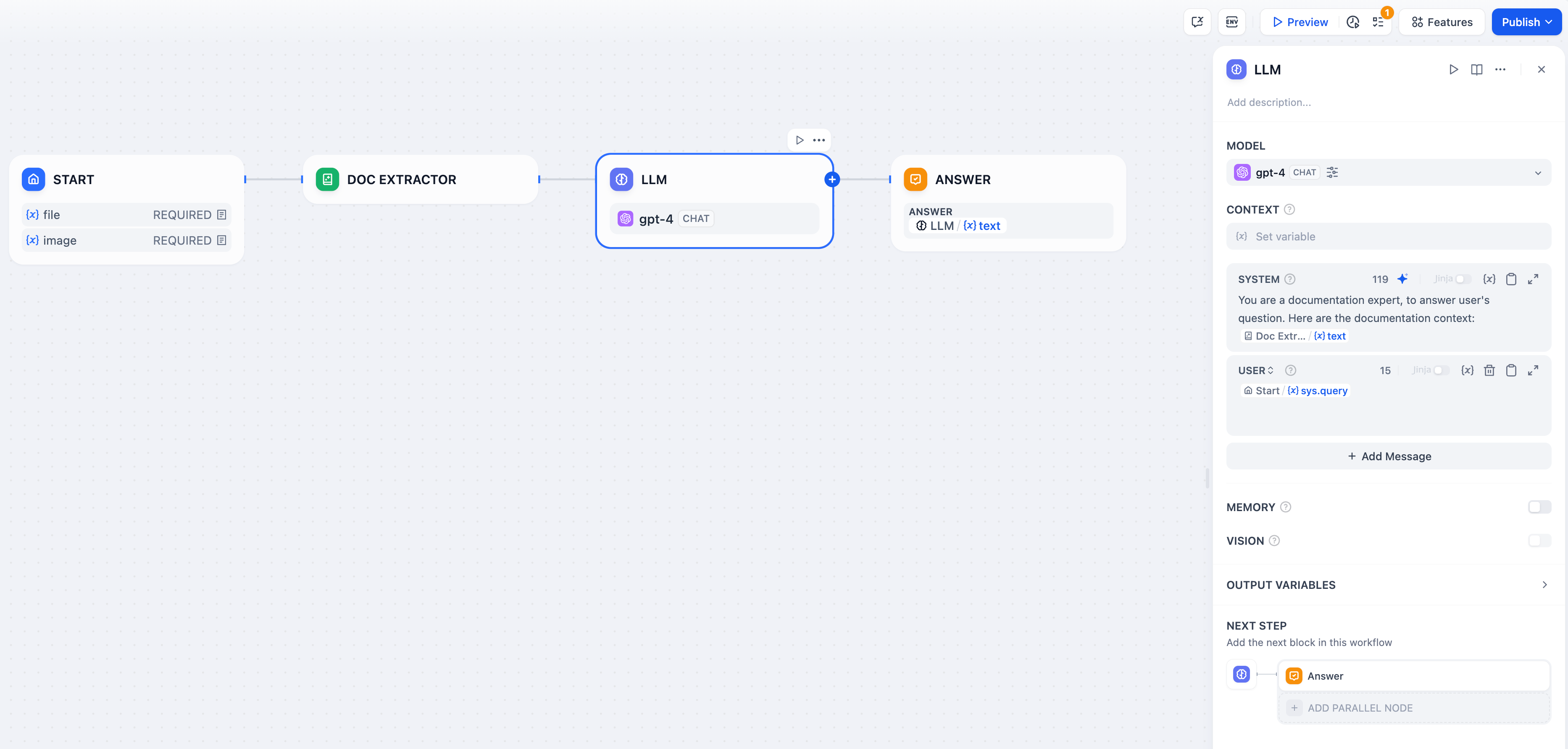
Configuration Process:
- Enable file upload for the application. Add a single file variable in the “Start” node and name it
pdf. - Add a document extractor node and select the
pdfvariable in the input variables. - Add an LLM node and select the output variable of the document extractor node in the system prompt. The LLM can read the contents of the file through this output variable.
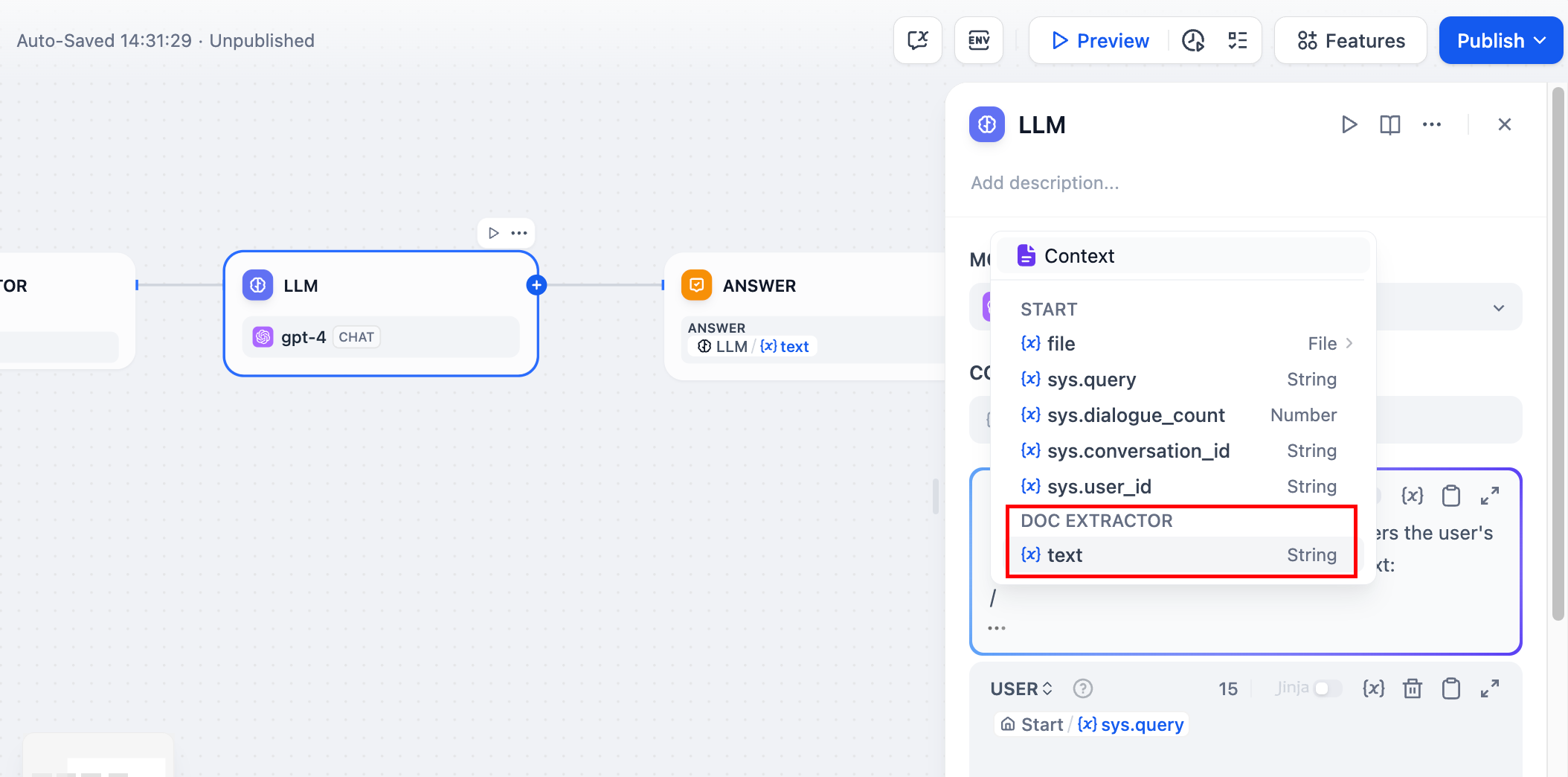
Configure the end node by selecting the output variable of the LLM node in the end node.
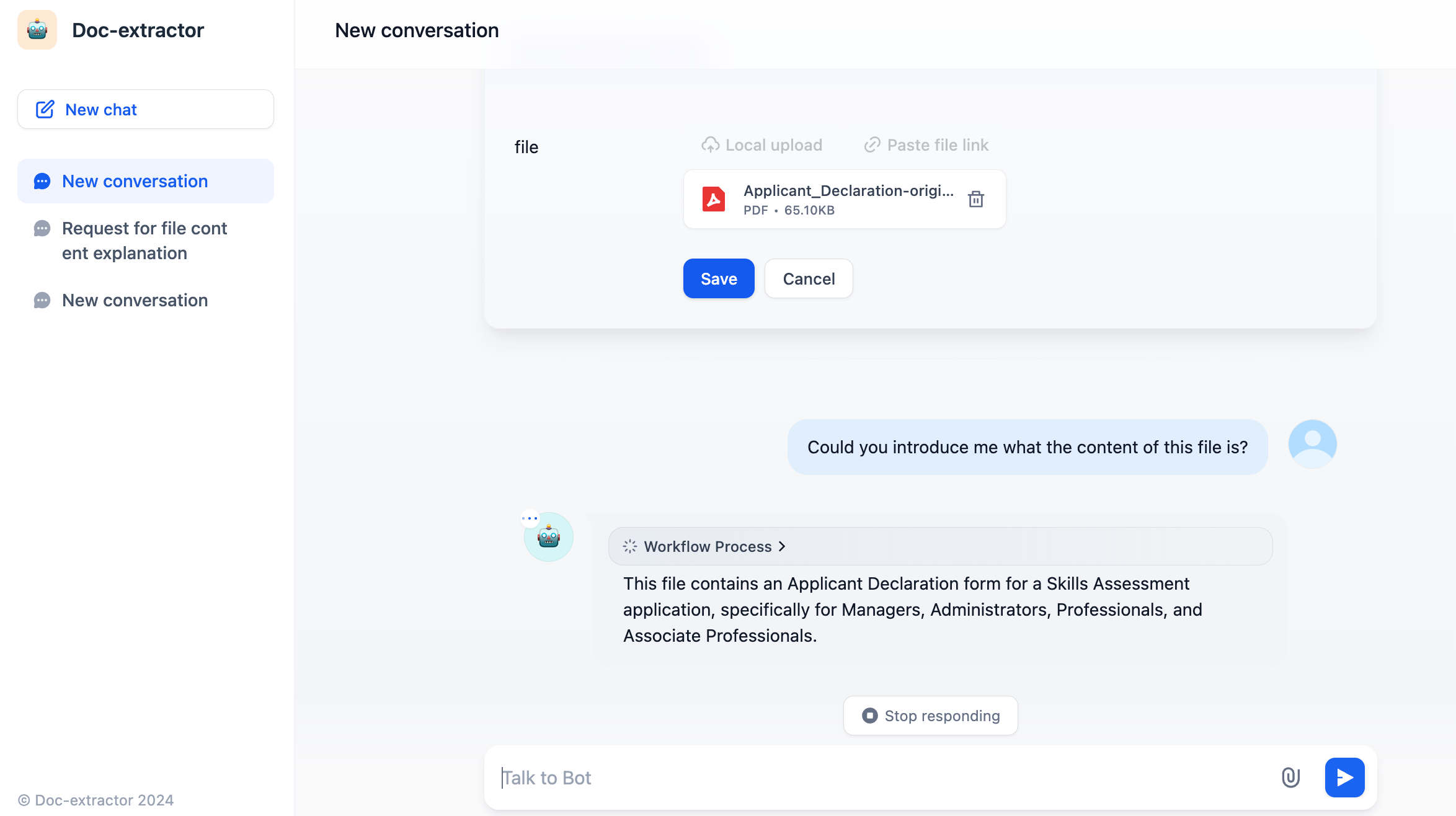
After configuration, the application will have file upload functionality, allowing users to upload PDF files and engage in conversation.
For how to upload files in chat conversations and interact with the LLM, please refer to Additional Features.

