System Settings
Single Sign-On
1. Function Overview
To enhance system security and enterprise-level identity management capabilities, the Admin Dashboard now supports Single Sign-On (SSO) functionality. By configuring the enterprise’s identity provider, administrators can achieve a unified login portal, simplify user management processes, and eliminate the need to maintain separate credentials. The system supports three identity authentication protocols: SAML, OIDC, OAuth2.2. Operating Instructions
2.1 Access Path
Admin Dashboard > Settings > Single Sign-On.
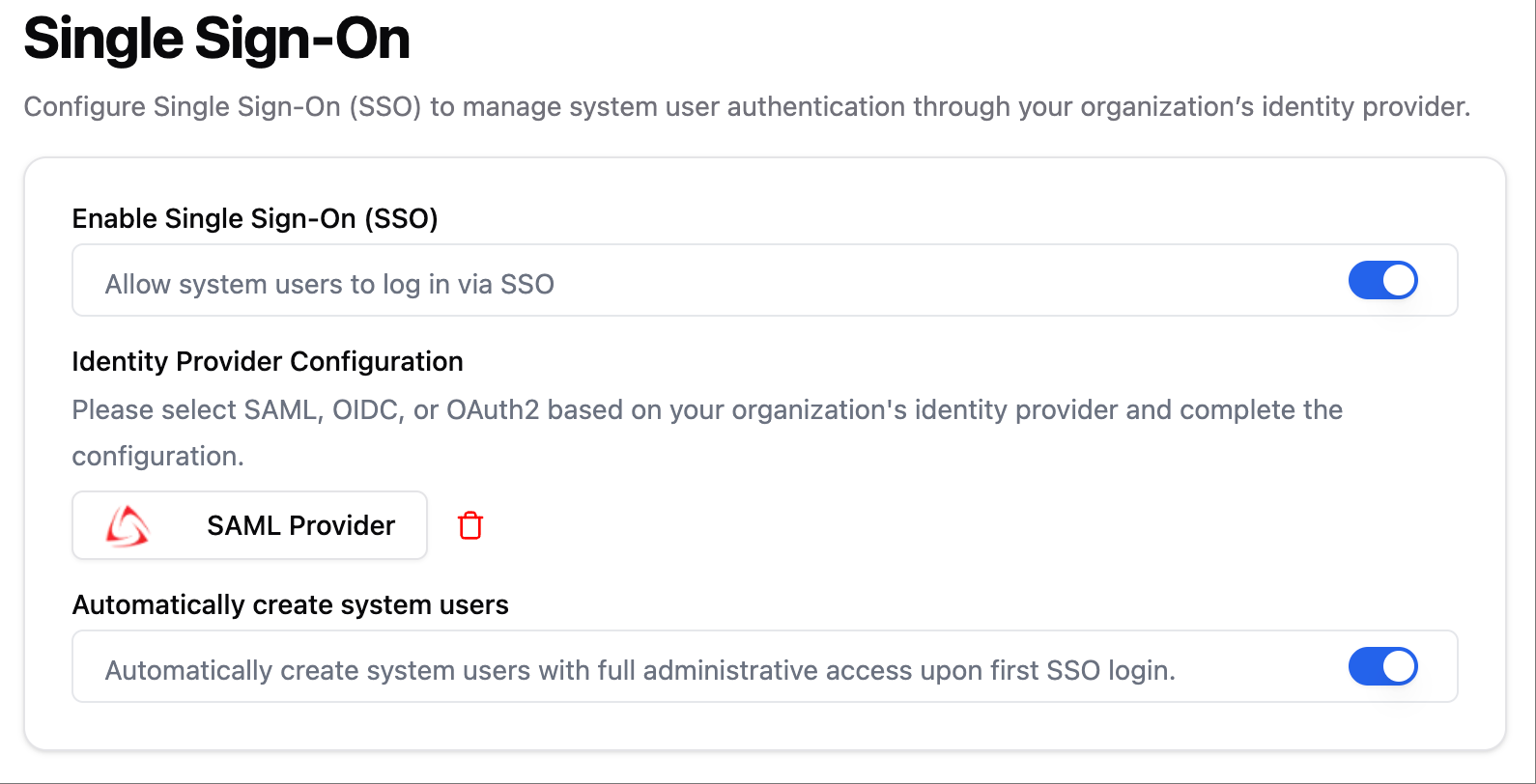
2.2 Enable / Disable SSO Functionality
On the SSO page, administrators can enable or disable the system’s SSO login capability via a toggle switch.- When enabled, the login page displays the “Login with SSO” option;
- When disabled, the system no longer shows the SSO login option, but local account login remains unaffected.
2.3 Configure Identity Provider
Integration with the enterprise’s existing identity system is supported through SAML, OIDC, and OAuth2 protocols. Administrators can select the protocol type based on the identity system used by the enterprise and fill in the corresponding fields (such as Client ID, Issuer URL, certificate, etc.). Configuration methods for the three protocols can be referenced in theIdentity Authentication module’s SSO configuration:
- Okta
- Azure
- GitHub
2.4 Automatically Create System Users
When this option is enabled, users logging in for the first time via SSO will automatically create a system user, without requiring manual account creation.- The created users will have full system management permissions;
- The current system does not have a role management mechanism, and all users have the same permissions.
3. Login Behavior Description
| Login Method | Condition | Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Local Login | Always available | Account password login |
| SSO Login | SSO enabled and identity provider configured | ”Login with SSO” option displayed on login page |
| First SSO Login | When automatic system user creation is enabled | Automatically create and log into the system |
4. Precautions
- Do not enable the SSO switch before the identity provider configuration is successful;
- The system currently does not support permission differentiation after user login, and all system users default to super administrator privileges.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between SSO in Admin Dashboard > Settings and SSO in Authentication > Members?
The single sign-on functionalities are targeted at different user groups and applicable to different login scenarios:
-
Admin Dashboard SSO (
Admin Dashboard > Settings > Single Sign-On) Used to configure the authentication method for system administrators (System Users) accessing the Admin Dashboard, typically aimed at enterprise technical personnel or platform operators with system management permissions. -
Member Authentication SSO (
Authentication > Members) Used to configure identity authentication for workspace members or Web application end users, applicable to business end users, customers, employees, etc., accessing the business workspace or Web product front-end login scenarios.
Q2: What are the differences in configuration at the enterprise IdP (identity provider) end for these two SSO functionalities?
To distinguish between the identity authentication of the Admin Dashboard and business applications, it is recommended to configure two separate applications in the enterprise IdP:- Backend SSO Configuration: Used for identity authentication of the Admin Dashboard, assigned to users with system management permissions (such as administrators, DevOps, platform operators);
- Member SSO Configuration: Used for identity authentication of workspace or Web application users, aimed at ordinary members, internal employees, customer users, etc.

